‘Explosive increase’ of ticks that cause meat allergy in US due to climate crisis
‘Explosive increase’ of ticks that cause meat allergy in US due to climate crisis

www.theguardian.com
‘Explosive increase’ of ticks that cause meat allergy in US due to climate crisis
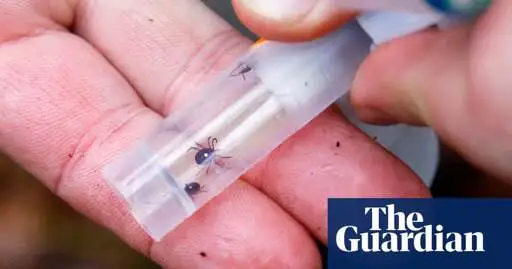
Unusually aggressive lone star ticks, common in the south-east, are spreading to areas previously too cold for them